PRE-REQUISITES :
Amazon Cognito User Pool has already been set up.
HOW TO USE COGNITO WITH LARAVEL APPLICATION?
Step 1: Click on the user pool and store a few details in the Laravel .env file of your project
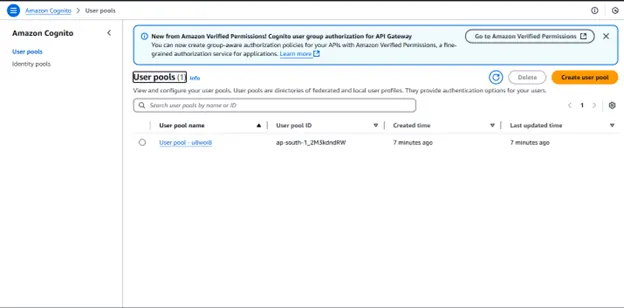
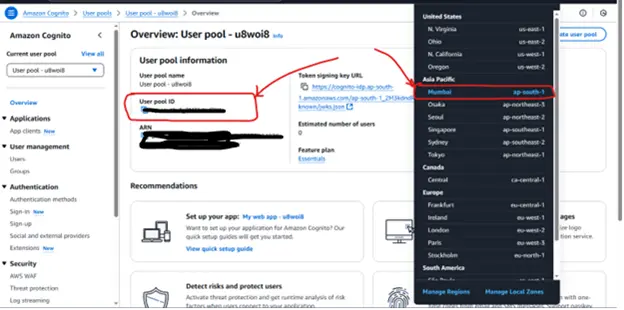
AWS_USER_POOL_ID = your-account-user-pool-id
AWS_USER_POOL_REGION = your-account-region
Click on app clients and get the following details
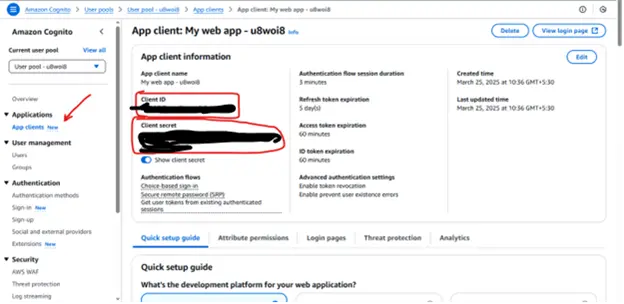
AWS_APP_CLIENT_ID = your-app-client-id
AWS_APP_CLIENT_SECRET_ID = your-app-client-secret-id
Step 2: Return to the AWS home console and select Security Credentials.
Step 3: Click on Create Access Key
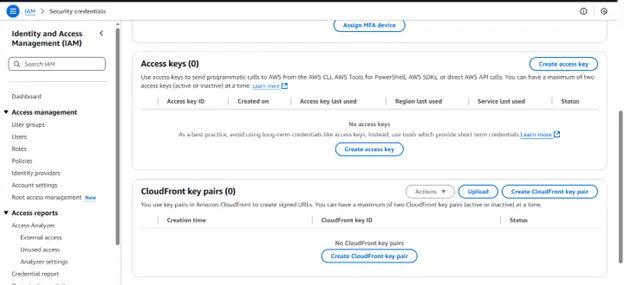
Step 4: After downloading and storing the keys in.csv format, add them to the project’s env file, which already has the AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY parameters by default. You should also comment out the AWS_DEFAULT_REGION parameter.
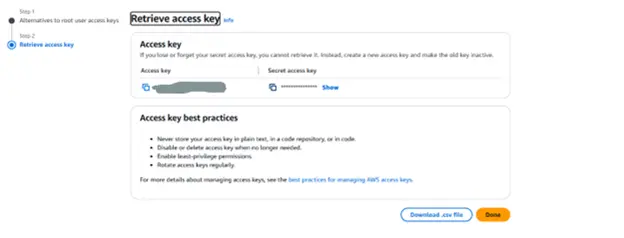
Step 5: To add any of the authentication flows labeled ALLOW_USER_PASSWORD_AUTH, ALLOW_ADMIN_USER_PASSWORD_AUTH, or ALLOW_CUSTOM_AUTH, click the Edit button on the app client. For the sake of illustration, we are currently choosing each one.
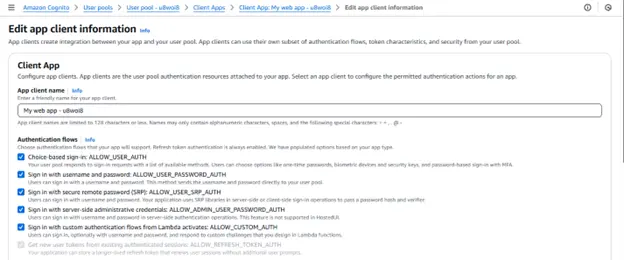
Step 6: Use the AWS console’s search box to look up Lambda.
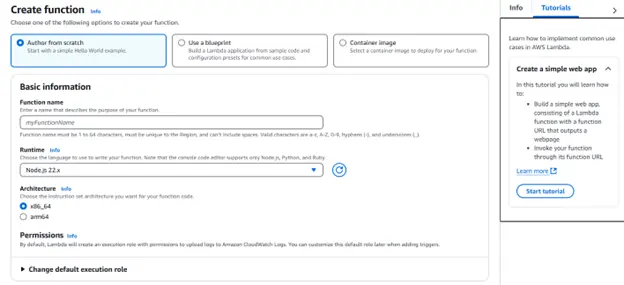
Step 7: Click on the Create function button which will show this page.
Enter the function name of your choice.
Select run-time language or the language function would be written in. For now, we are choosing python and then click on create function.
Step 8: You will be redirected to this page
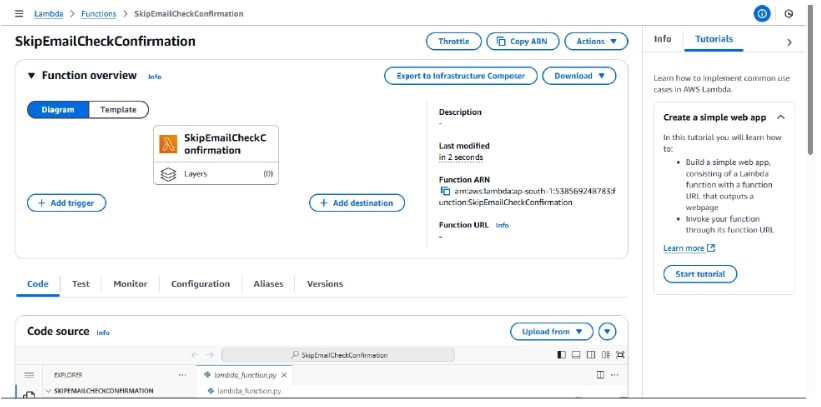
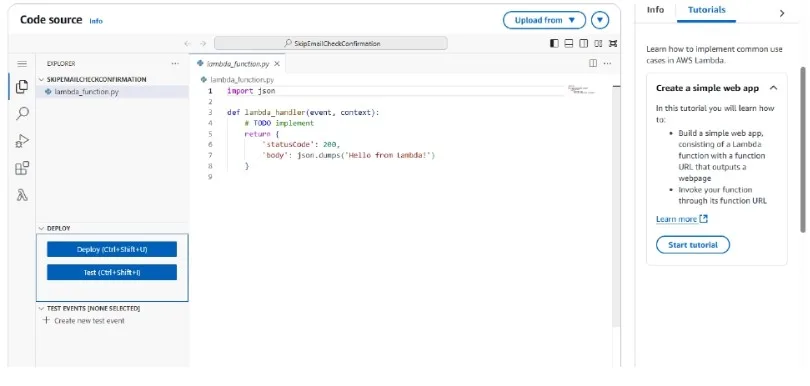
To make the function useable, add the code below to the lambda_function.py file and click deploy.
import json
def lambda_handler(event, context):
event['response']['autoConfirmUser'] = True
event['response']['autoVerifyEmail'] = True
return event
Step 9: Go back to the AWS Cognito console home, then click on “Extensions”, and select “Add Lambda Trigger”.
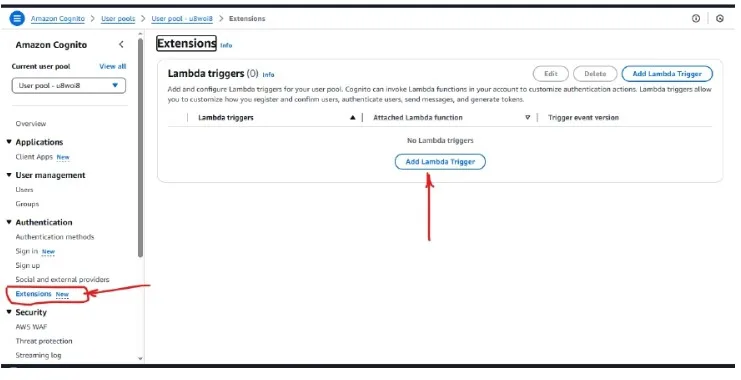
Step 10: Set up the Lambda Trigger
In this step, we’ll use the sign-up trigger because we want the Lambda function to execute during the user sign-up process.
Specifically, we are using a pre-sign-up trigger, which means the Lambda function will run before the user is registered in AWS Cognito.
You can choose a different trigger type based on your specific requirements.
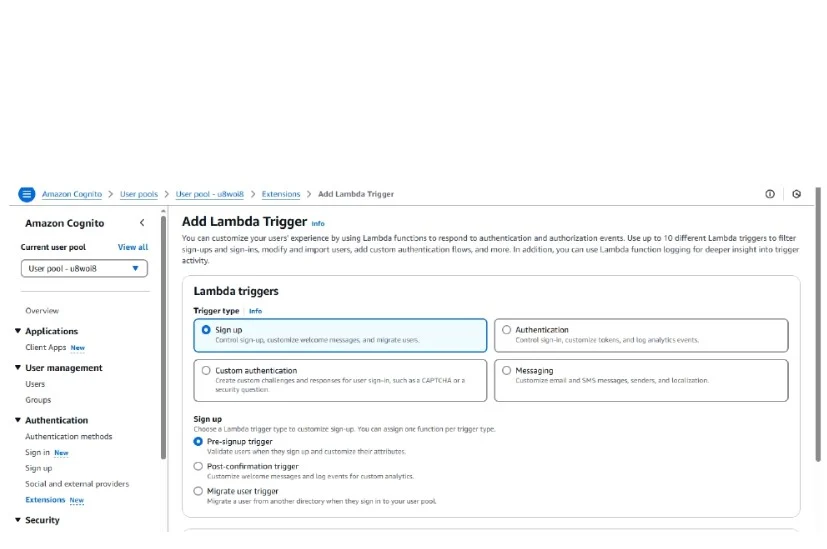
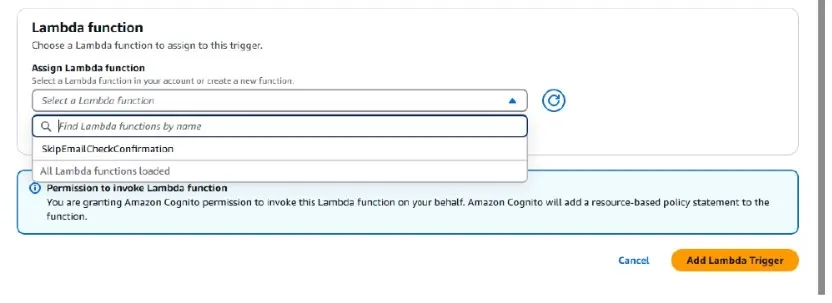
Select the appropriate Lambda function you created earlier and click on
“Add Lambda Trigger”
.
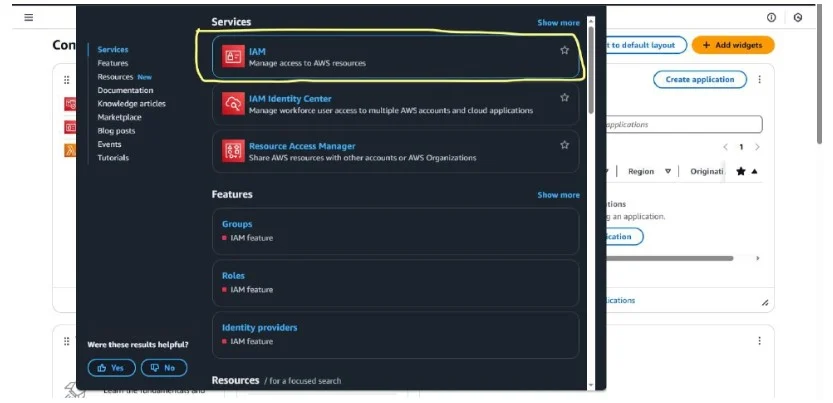
Step 11: Now, search for IAM in the AWS Console search bar
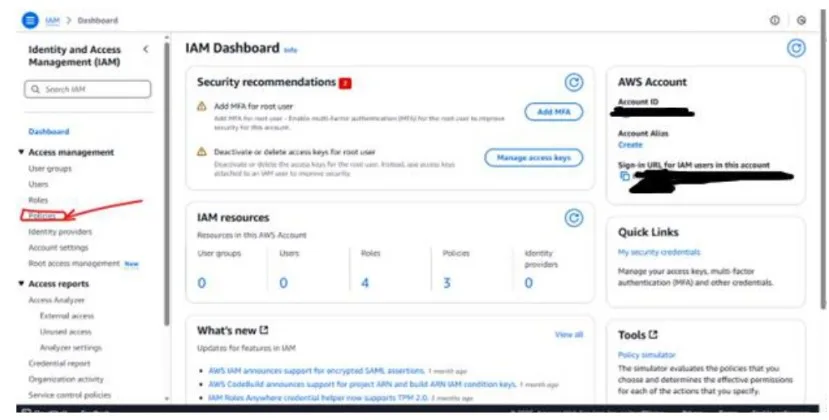
Step 12:Click on it and go to the Policies section
Click on create policy button.
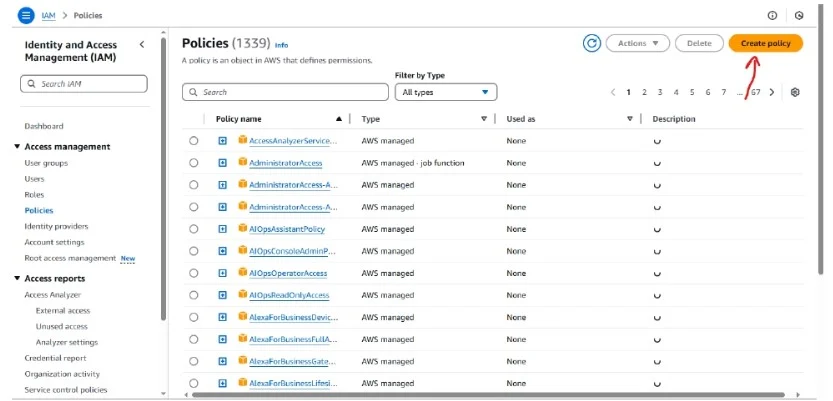
Choose a service named Cognito user pool in the below given image
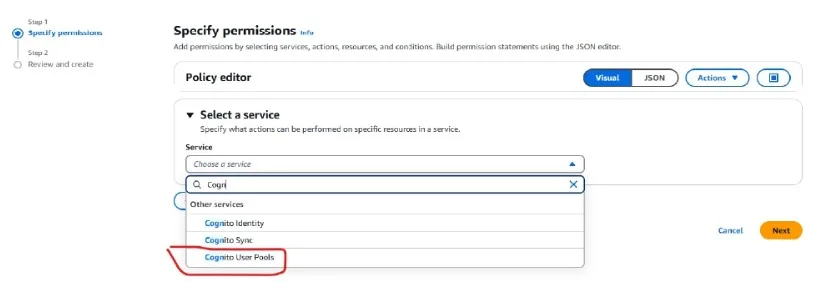
Select the checkbox
Here, we have provided all the permissions to the policy we are creating.
You can choose permissions as per your requirement. Then you need not click on the Checkbox Which provides all the permissions to the policy.
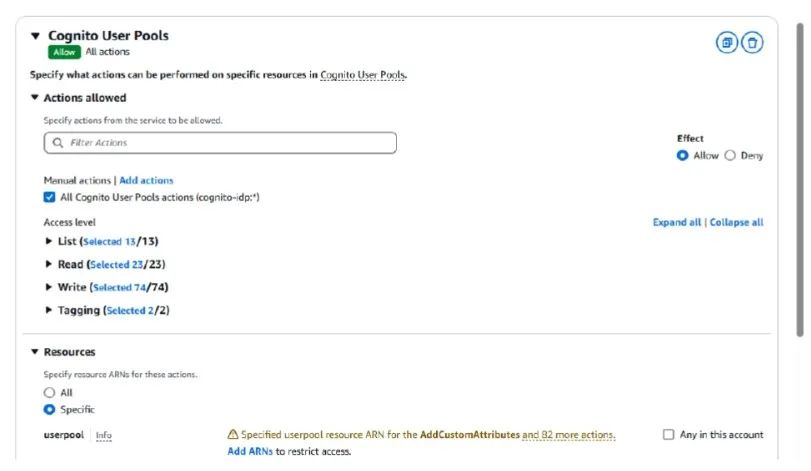
Go to cognito console and fetch the arn for your user pool and add it in the Resources section of the policy being created by clicking
Add ARNs
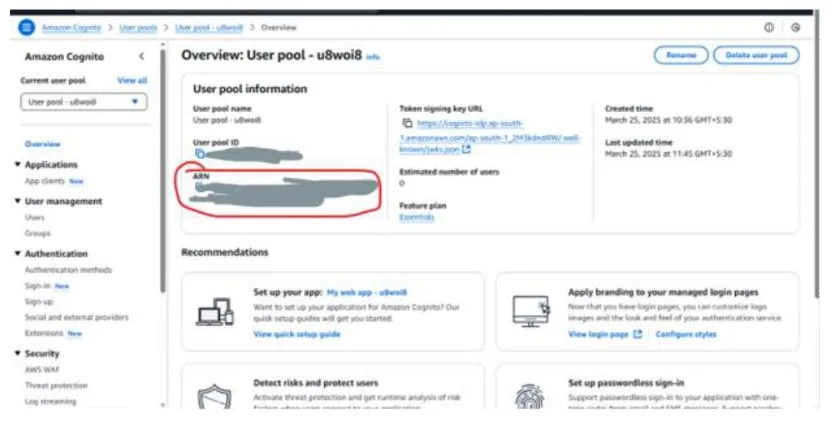
Add your copied ARN in the field named resource arn. Also when add arn is clicked it will open this box
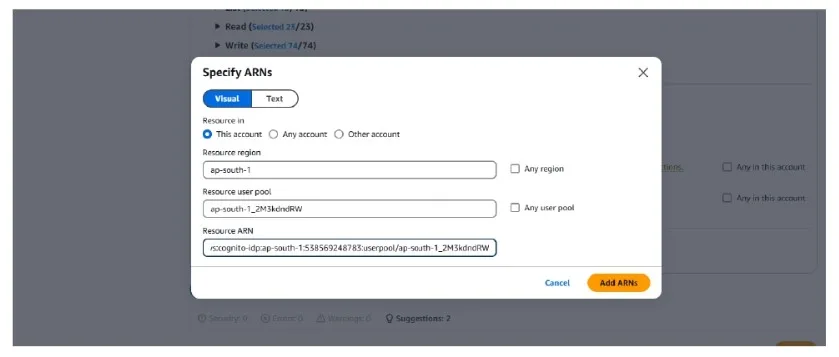
Then Click next
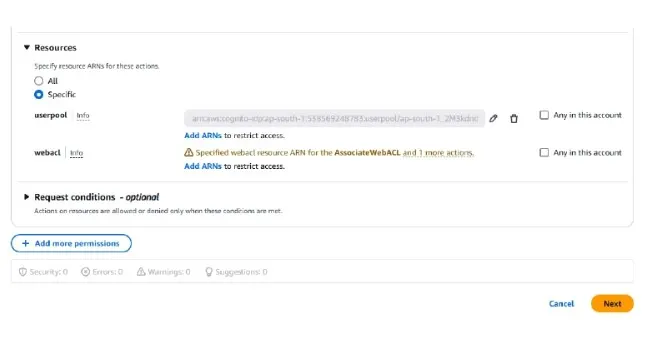
Add the policy name and description (optional)
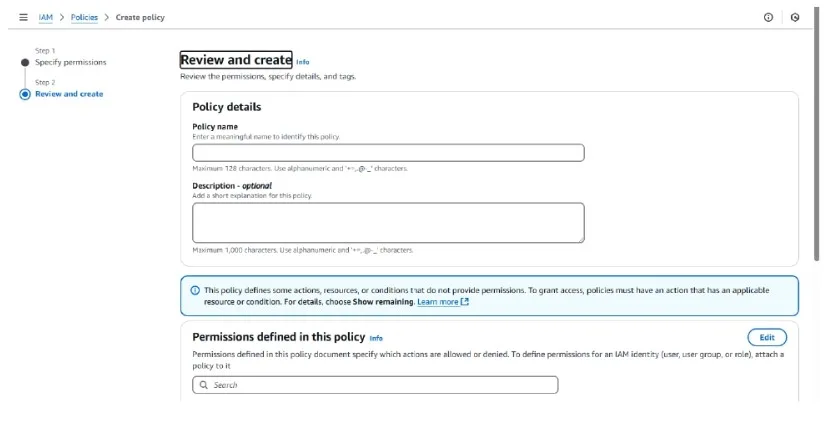
Then click on create policy
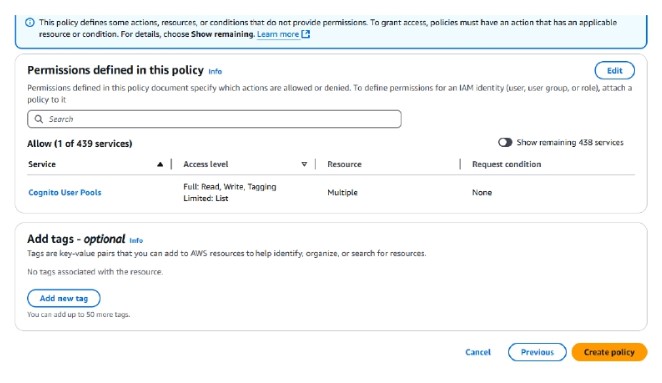
After that Search in the search bar for the policy name, click it and go to Attach entities
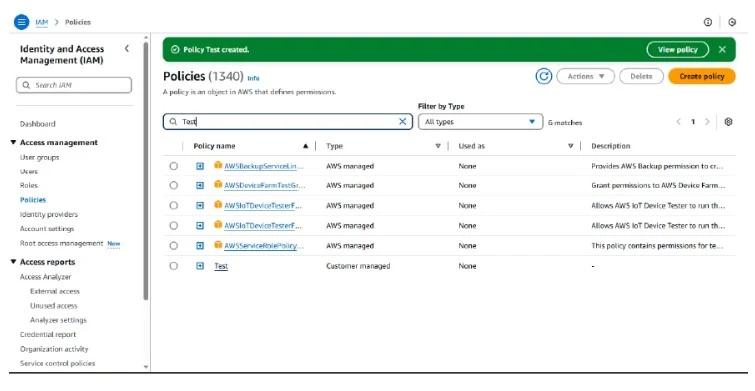
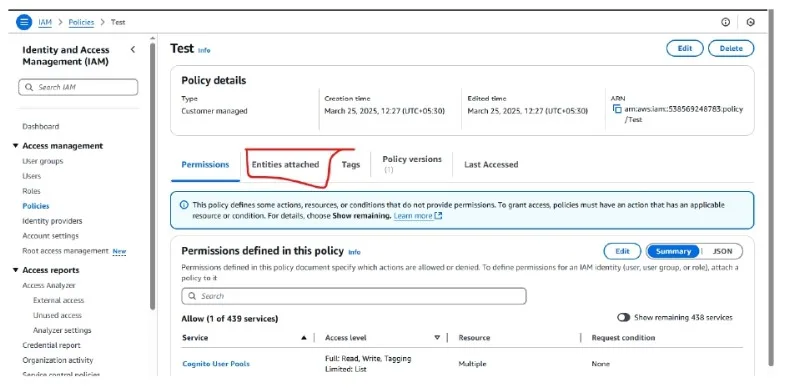
Click on attach and add the role of your lambda function
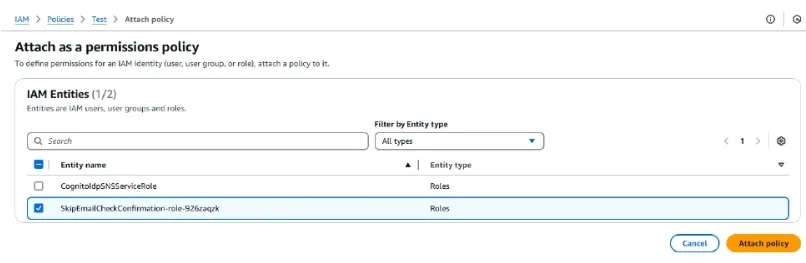
Then click on attach policy.
Step 13: Go to roles section and you will be able to see the policies attached to your roles of lambda function.
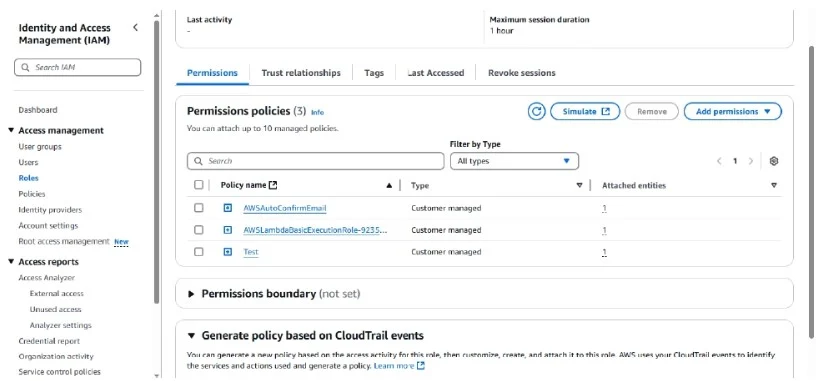
Step 14: Add required Packages
a. Add aws sdk for php using command composer require aws/aws-sdk-php
b. Add Firebase jwt token sdk for php by using command composer require firebase/php-jwt.
Step 15: Create a controller file.
Demo controller file code:
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers\Cognito;
use App\Http\Controllers\Controller;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use App\Services\CognitoAuthService;
class CognitoAuthController extends Controller
{
//
protected $cognitoAuth;
public function __construct(CognitoAuthService $cognitoAuth)
{
$this->cognitoAuth = $cognitoAuth;
}
public function register(Request $request)
{
$request->validate([
'name' => 'required|string|max:255',
'email' => 'required|string|email|max:255|unique:users',
'password' => 'required|string|min:6|confirmed',
]);
return response()->json($this->cognitoAuth->registerUser(
$request->name,
$request->email,
$request->password
));
}
public function login(Request $request)
{
// Validate the request input
$request->validate([
'email' => 'required|email',
'password' => 'required|string|min:6',
]);
// Call the service method with extracted email & password
return $this->cognitoAuth->loginUser($request->email, $request->password);
}
public function user(Request $request)
{
$accessToken = $request->header('Authorization');
if (!$accessToken) {
return response()->json(['error' => 'Token missing'], 401);
}
return response()->json($this->cognitoAuth->getUser(str_replace('Bearer ', '', $accessToken)));
}
public function logout(Request $request)
{
$accessToken = $request->header('Authorization');
//dd($accessToken);
if (strpos($accessToken, 'Bearer ') === 0) {
$accessToken = substr($accessToken, 7); // Remove "Bearer " prefix
}
return response()->json($this->cognitoAuth->logoutUser($accessToken));
}
}
Step 16: Create a Service Class
Demo Service Class code:
<? php
namespace App\Services;
use Aws\CognitoIdentityProvider\CognitoIdentityProviderClient;
use Exception;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
class CognitoAuthService {
protected $client;
public function __construct() {
$this -> client = new CognitoIdentityProviderClient([
'version' => 'latest',
'region' => env('AWS_COGNITO_REGION'),
]);
}
/**
* Generate Secret Hash for Cognito authentication.
*/
private function getSecretHash($username) {
return base64_encode(
hash_hmac('sha256', $username.env('AWS_COGNITO_CLIENT_ID'), env('AWS_COGNITO_CLIENT_SECRET'), true)
);
}
/**
* Register a new user in Cognito.
*/
public function registerUser($name, $email, $password) {
try {
$username = explode('@', $email)[0];
$response = $this -> client -> signUp([
'ClientId' => env('AWS_COGNITO_CLIENT_ID'),
'Username' => $username,
'Password' => $password,
'SecretHash' => $this -> getSecretHash($username),
'UserAttributes' => [
['Name' => 'name', 'Value' => $name],
['Name' => 'email', 'Value' => $email],
],
]);
// Check if Cognito confirms the user (Lambda trigger may be failing)
$userConfirmed = $response['UserConfirmed'] ?? false;
return response() -> json([
'message' => 'User registered successfully.',
'userConfirmed' => $userConfirmed,
'cognitoResponse' => $response
]);
} catch (\Exception $e) {
return response() -> json([
'error' => 'AWS Cognito Error: '.$e -> getMessage()
], 400);
}
}
/**
* Authenticate user with Cognito.
*/
public function loginUser($email, $password) {
try {
$result = $this -> client -> initiateAuth([
'AuthFlow' => 'USER_PASSWORD_AUTH',
'ClientId' => env('AWS_COGNITO_CLIENT_ID'),
'AuthParameters' => [
'USERNAME' => $email,
'PASSWORD' => $password,
'SECRET_HASH' => $this -> getSecretHash($email), // Important if client has a secret
],
]);
return [
'message' => 'Login successful',
'token' => $result['AuthenticationResult']['AccessToken'],
'refresh_token' => $result['AuthenticationResult']['RefreshToken'],
'id_token' => $result['AuthenticationResult']['IdToken']
];
} catch (Exception $e) {
return ['error' => $e -> getMessage()];
}
}
/**
* Get authenticated user details.
*/
public function getUser($accessToken) {
try {
$user = $this -> client -> getUser([
'AccessToken' => $accessToken,
]);
return [
'username' => $user['Username'],
'attributes' => $user['UserAttributes']
];
} catch (Exception $e) {
return ['error' => 'Invalid or expired token'];
}
}
/**
* Refresh user token.
*/
public function refreshToken($refreshToken) {
try {
$result = $this -> client -> initiateAuth([
'AuthFlow' => 'REFRESH_TOKEN_AUTH',
'ClientId' => env('AWS_COGNITO_CLIENT_ID'),
'AuthParameters' => [
'REFRESH_TOKEN' => $refreshToken,
'SECRET_HASH' => $this -> getSecretHash($refreshToken),
],
]);
return [
'message' => 'Token refreshed successfully',
'token' => $result['AuthenticationResult']['AccessToken']
];
} catch (Exception $e) {
return ['error' => $e -> getMessage()];
}
}
/**
* Logout user from Cognito.
*/
public function logoutUser($accessToken) {
try {
// Validate access token format
if (!$accessToken || !preg_match('/^[A-Za-z0-9-_=.]+$/', $accessToken)) {
return ['error' => 'Invalid or missing access token'];
}
// Perform global sign-out
$this -> client -> globalSignOut([
'AccessToken' => $accessToken,
]);
return ['message' => 'User logged out successfully'];
} catch (AwsException $e) {
return ['error' => $e -> getAwsErrorMessage()];
} catch (Exception $e) {
return ['error' => $e -> getMessage()];
}
}
}Step 17: Create routes:
Demo routes :
<? php
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Route;
use App\Http\Controllers\Cognito\CognitoAuthController;
Route:: prefix('cognito') -> group(function () {
Route:: post('/register', [CognitoAuthController:: class, 'register']);
Route:: post('/login', [CognitoAuthController:: class, 'login']);
Route:: get('/user', [CognitoAuthController:: class, 'user']);
Route:: post('/logout', [CognitoAuthController:: class, 'logout']);
});Step 18: Test routes on postman.
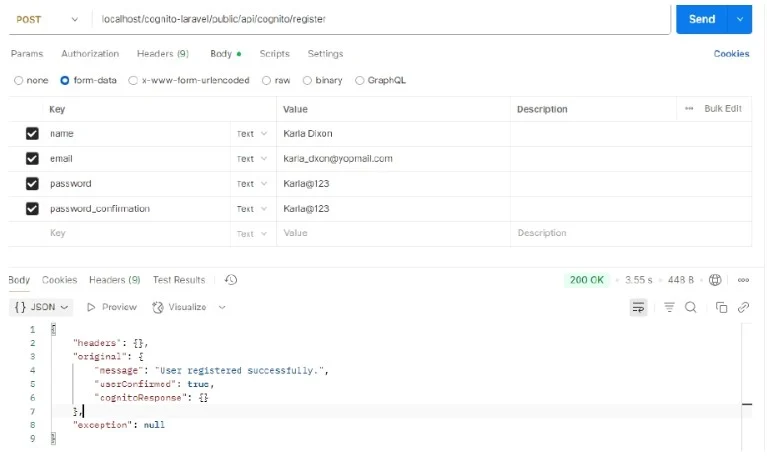
Test 1: Register user
Data field to be filled up in postman: name, email, password and password confirmation
Below is the image of the successful registration of user on the cognito user pool.
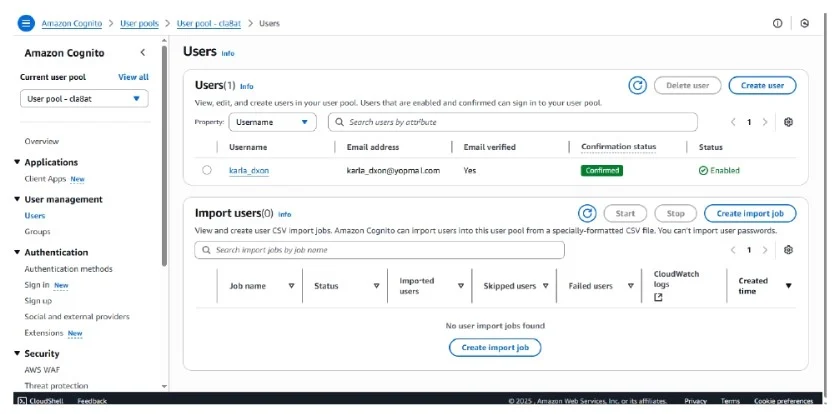
Test 2: Login User
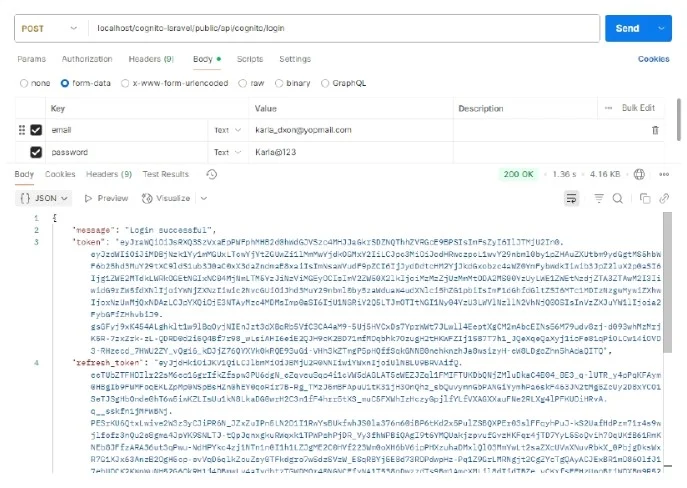
Data field being filled in postman: email,password
On successful login the cognito will provide access token and refresh token as shown in the response.
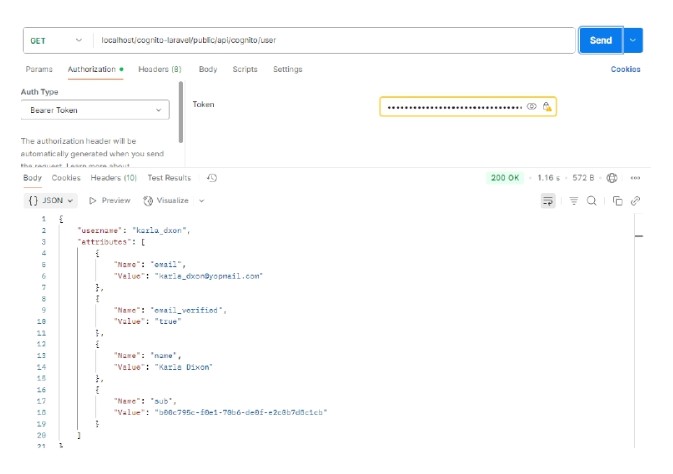
Test 3: Get user Details
Data fields being filled in postman: Authorization header-> bearer token, that means access token which we got in the login response
Successfully fetched details would look like below:
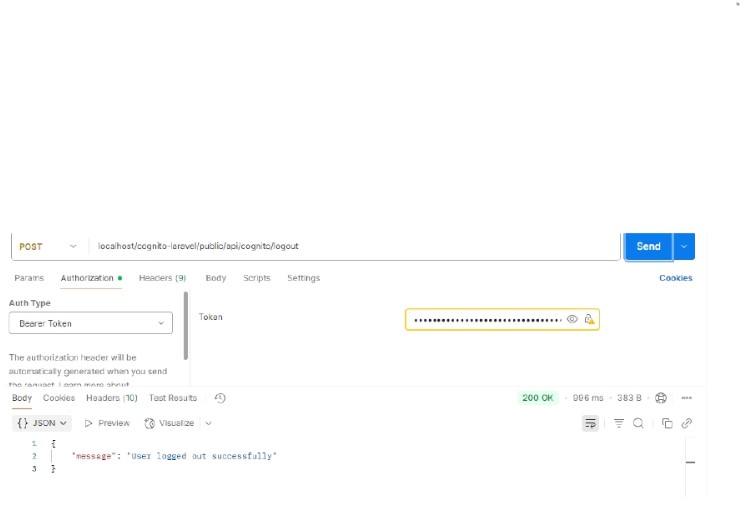
Test 4: Logout user
Data fields being used in the postman: Authorization header-> bearer token
Successfully logged out output would look like this:
STAY TUNED FOR MORE USEFUL BLOGS!!

