Pre-requisites:
- Laravel app installed through composer create-project laravel/laravel your-project-name. Also, a package installed through composer require aws/aws-sdk-php.
- Account on aws with following credentials saved in the .env file of the project
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID, AWS_ACCESS_SECRET_KEY, AWS_DEFAULT_REGION.
How to Configure AWS Secrets Manager?
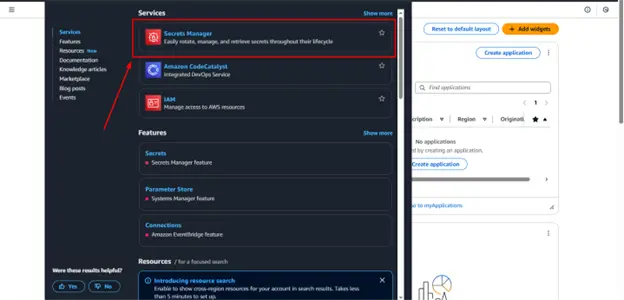
Step 1: Open AWS Secrets Manager
- Sign into the AWS Management Console.
- Search for Secrets Manager and open it.
Step 2: Store a New Secret
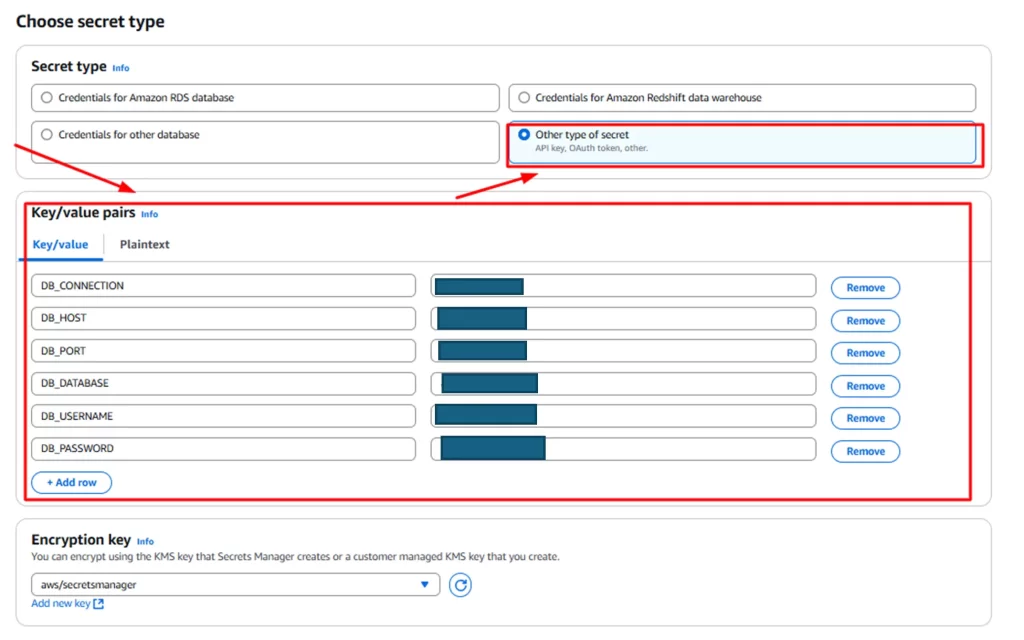
- Click “Store a new secret”.
- Choose secret type (e.g., credentials for RDS, other types, or plain text).

Step 3: Configure the Secret
- Provide the name of the secret to be made, optionally provide the description for the secret.
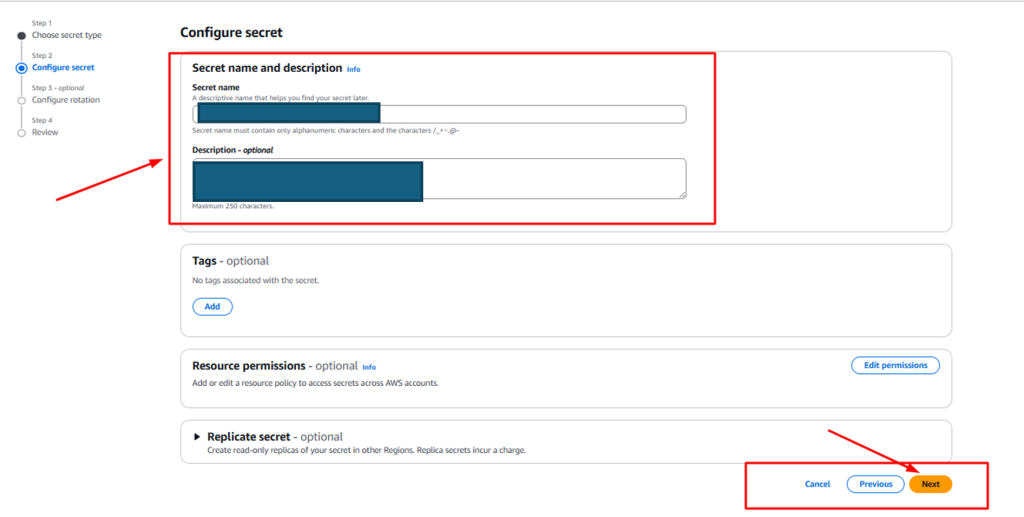
Step 4: Create a rotation schedule for your secret(optional).
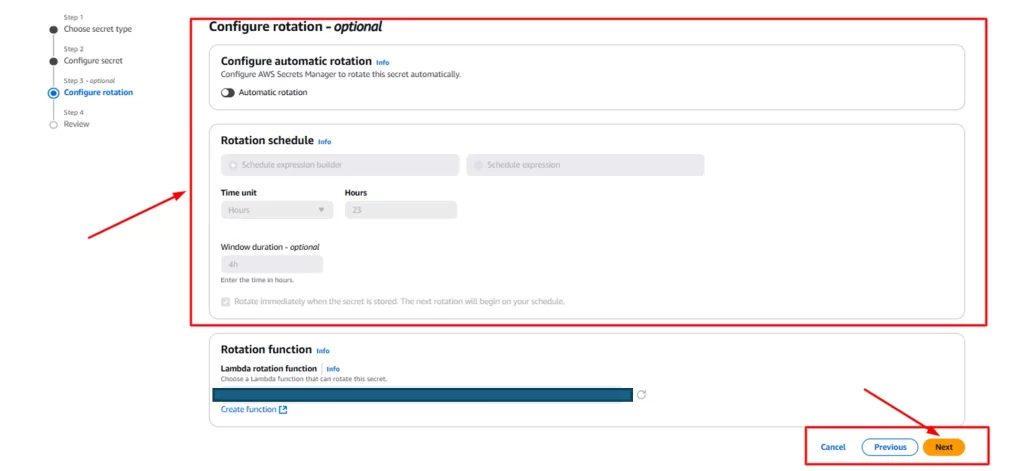
Step 5: Review the configuration of the secret you created.
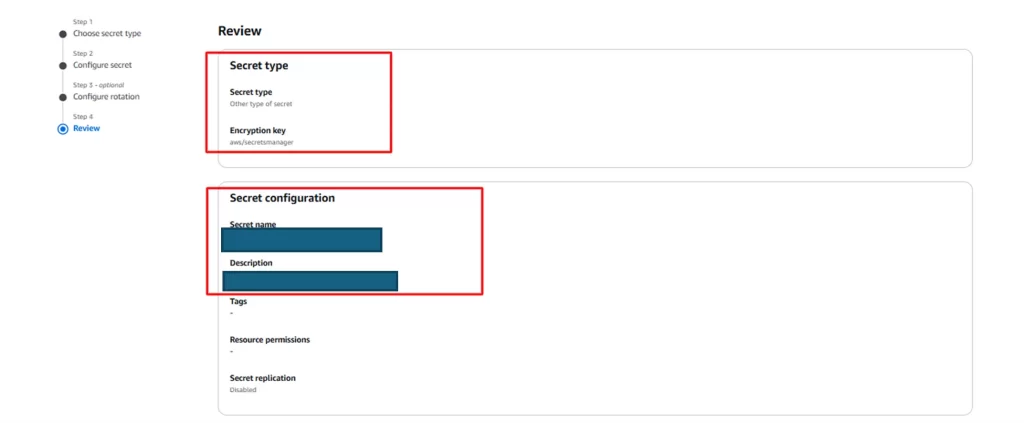

How to configure IAM for Secrets Manager?
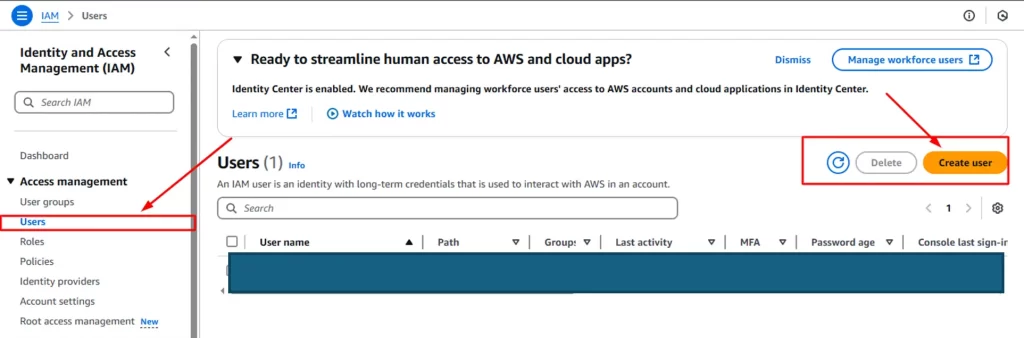
Step 1: Search for IAM in the aws console search bar.
- Go for users menu in the sidebar
- Click on create user button to create the user
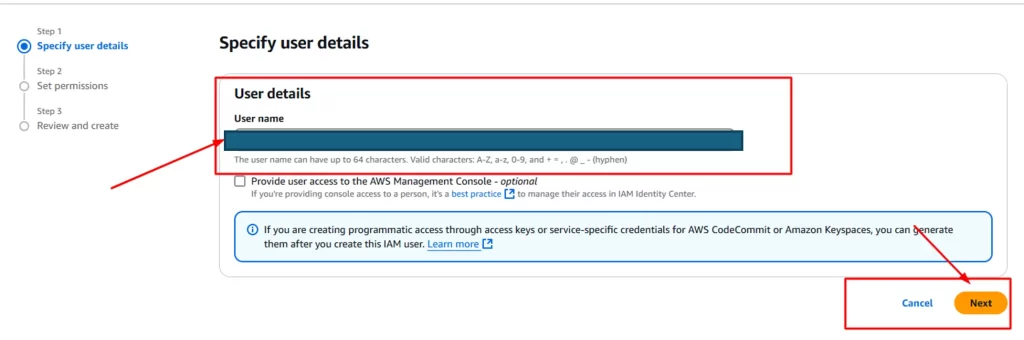
Step 2: Provide the user details
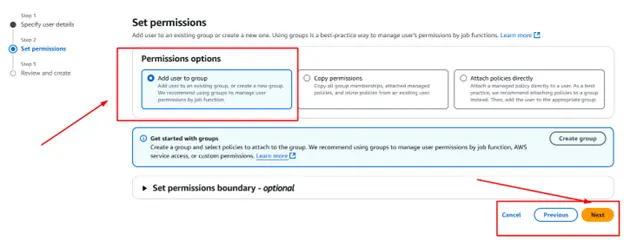
Step 3: Set the user permission for the secrets manager being created.
Step 4: Review the details entered for creating the user and click on the Create user button to create the user.
Step 5: Once user
Step 6: Clicking on the user’s name in the table will take you to this page to add the permissions for the user.
• Click on add permissions.
• Select Create inline policy.
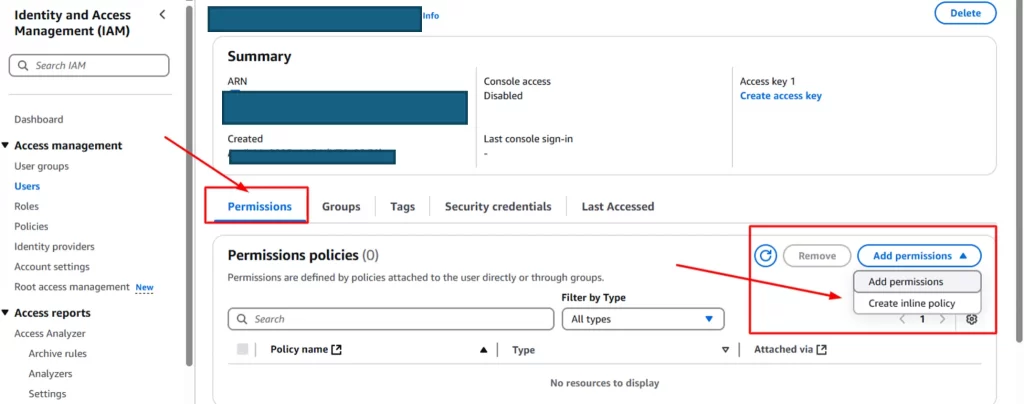
Step 7: Specify the permissions for the policy
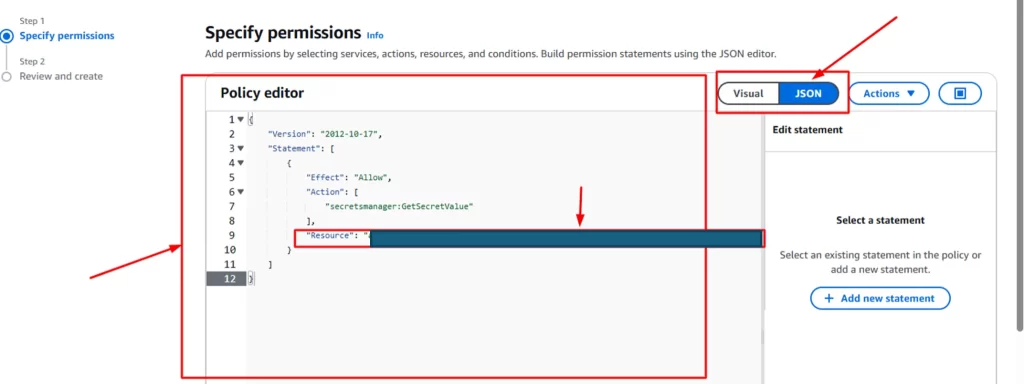
Step 8: To specify what resource to be included in the permission, go back to the Secrets Manager console.
- Click on the name of the secret.It will take to the details of the secret. And it contains Secret ARN. Copy it and put it in the policy’s resource parameter.


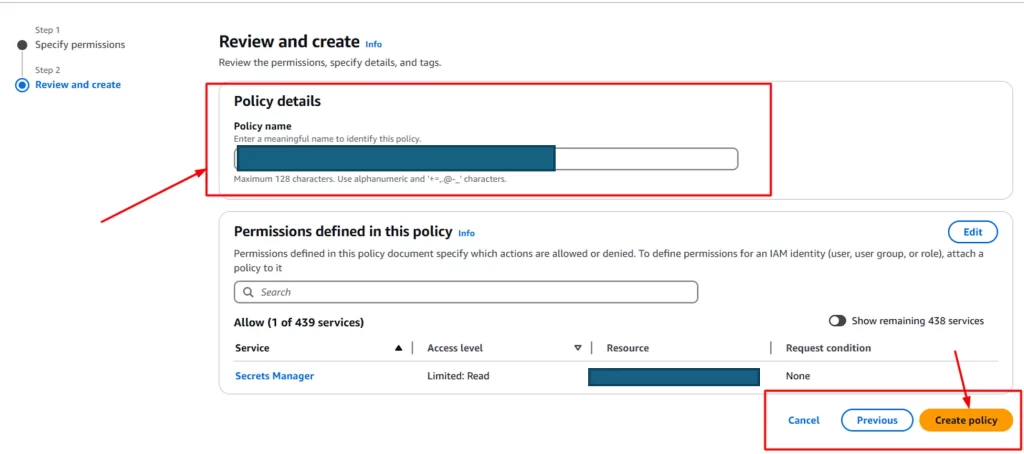
Step 9: Review the policy and click on create policy button. It will be attached to the users

Laravel App
Step 1: Create a service provider class like this:
<?php
namespace App\Services;
use Aws\SecretsManager\SecretsManagerClient;
use Aws\Exception\AwsException;
class SecretsManagerService
{
protected $client;
public function __construct()
{
$this->client = new SecretsManagerClient([
'version' => 'latest',
'region' => 'your-aws-default-region',
]);
}
public function getSecret(string $secretName)
{
try {
$result = $this->client->getSecretValue([
'SecretId' => $secretName,
]);
if (isset($result['SecretString'])) {
return json_decode($result['SecretString'], true);
}
} catch (AwsException $e) {
report($e);
return null;
}
}
}Step 2: Create a controller by running a command: php artisan make:controller nameOfYourController The ideal controller would look like this
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use App\Services\SecretsManagerService;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
class AwsSecretsManagerController extends Controller
{
//
public function index(SecretsManagerService $secretManager)
{
$data = $secretManager->getSecret('local/aws-secrets/databaseCredentials');
if($data){
return view('index');
}else{
echo "There is some issue";
}
}
}
Step 3: Create a blade file for confirming whether the output is seen in the view if credentials are matched.
The ideal blade file would look like this:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>AWS SECRETS</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>Hurray you made it here through secrets manager of aws.</h3>
</body>
</html>
Step 4: Look for database.php file and make changes in it like configuration of the connection driver you are using for the project.
For me its mysql so here’s an example of it.
<?php
use Illuminate\Support\Str;
use App\Services\SecretsManagerService;
$secrets = app(SecretsManagerService::class)->getSecret('local/aws-secrets/databaseCredentials');
return [
'default' => $secrets['DB_CONNECTION'],
'connections' => [
'mysql' => [
'driver' => 'mysql',
'url' => env('DB_URL'),
'host' => $secrets['DB_HOST'],
'port' => $secrets['DB_PORT'],
'database' => $secrets['DB_DATABASE'],
'username' => $secrets['DB_USERNAME'],
'password' => $secrets['DB_PASSWORD'],
'unix_socket' => env('DB_SOCKET', ''),
'charset' => env('DB_CHARSET', 'utf8mb4'),
'collation' => env('DB_COLLATION', 'utf8mb4_unicode_ci'),
'prefix' => '',
'prefix_indexes' => true,
'strict' => true,
'engine' => null,
'options' => extension_loaded('pdo_mysql') ? array_filter([
PDO::MYSQL_ATTR_SSL_CA => env('MYSQL_ATTR_SSL_CA'),
]) : [],
],
],
];
Step 5: Create a route in the web.php file like this
<?php
use App\Http\Controllers\AwsSecretsManagerController;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Route;
Route::get('/test-secret', [AwsSecretsManagerController::class, 'index']);Step 6: Hit the route in the browser and see the output. If the credentials are matched and connection is created then you will see the following output.
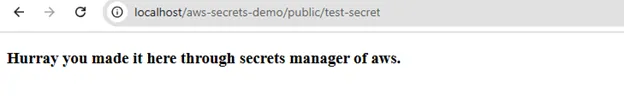
Else you might see the error message if credentials are null or not matched.
Conclusion
Integrating AWS Secrets Manager with Laravel provides a secure and scalable way to manage sensitive configuration data such as database credentials, API keys, and other secrets. By offloading secret management to AWS, you reduce the risk of exposing sensitive data in your codebase or configuration files. With a simple service class and controller setup, Laravel can efficiently fetch secrets on demand while keeping your application clean, secure, and compliant with best practices. As your application grows, this approach ensures that secret rotation, auditing, and access control can all be handled centrally and securely through AWS.
Ready to take your Laravel security to the next level? Start using AWS Secrets Manager today and keep your secrets safe!


